Q1. Water vapour passes out through stomata during translocation.
Solution
False
Water moves out of the stomata during transpiration.
Q2. (a) In summer, why do we find white patches on our clothes, especially in areas like underarms? (b) Describe the excretory products of birds and lizards.
Solution
(a) On a hot summer day, we sweat a lot. Sweat contains water and salts. The water of sweat evaporates, leaving behind the salts which appear as white patches on our clothes.(b) Birds and lizards excrete a semi-solid, white coloured compound, the uric acid.
Q3. During inhalation, ____________ gas fills up the lungs.
Solution
Oxygen
Q4. Draw the human excretory system and label any two of the following parts: kidney, urethra, ureter, urinary bladder.
Solution
Human Excretory System:
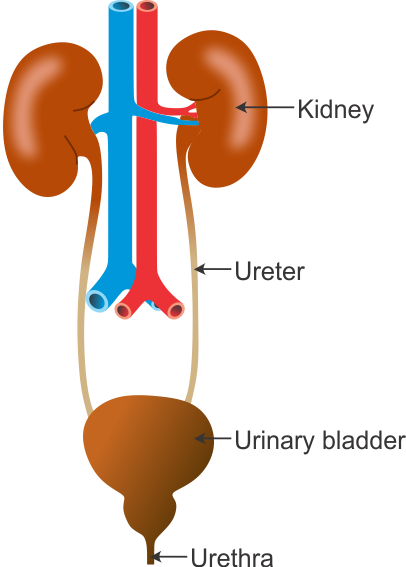 (Label any two parts)
(Label any two parts)
 (Label any two parts)
(Label any two parts)
Q5. Blood appears red due to the presence of haemoglobin.
Solution
True
Q6. Describe an activity to show transportation of water through cells.
Solution
i. Take a large potato, peel off its outer skin and cut one of its ends to make the base flat. ii. Now, make a deep and hollow cavity on the opposite side. iii. Fill half of the cavity with sugar solution and mark the level by inserting a pin in the wall of the potato. iv. Put the potato into a dish containing a small amount of water. Make sure that the level of water is below the level of the pin. v. Allow the apparatus to stand for few hours. vi. We would observe an increase in the level of sugar solution. This is because for very short distances water can move from one cell to another. In this way, water reaches xylem vessels of the root from the soil.
Q7. (a) What is vascular tissue? (b) What happens to the excessive water absorbed by roots?
Solution
(a) Vascular tissue is the tissue that conducts water and nutrients through the plant body in higher plants. Xylem and phloem are vascular tissues.(b) Some of the water absorbed by plant roots is used by the plants. But most of the water evaporates through the stomata present on the surface of leaves through transpiration.
Q8. Write the function of:(a) Xylem(b) Phloem
Solution
(a) Xylem transports water and nutrients in the plants.(b) Phloem transports food to all parts of the plant.
Q9. Give two functions of blood.
Solution
1. Blood carries oxygen from the lungs to the other cells of the body.
2. It transports waste for removal from the body.
Q10. A pair of ___________ carries the urine from urinary bladder to urethera.
Solution
Ureters
Q11. Differentiate between artery, vein and capillary.
Solution
Artery
Vein
Capillary
i. Thick-walled.
ii. Carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to other parts of the body.
i. Thin-walled.
ii. Carry carbon dioxide-rich blood from different organs to the heart.
i. Thin-walled.
ii. Capillaries are involved in the exchange of food material, respiratory gases, and body wastes.
Q12. A _________________ is a group of cells which perform a specialised function in an organism
Solution
tissue
Q13. Identify the instrument shown below.  Describe it.
Describe it.
 Describe it.
Describe it.Solution
The given instrument is the stethoscope. It consists of a chest piece that carries a sensitive diaphragm, two ear pieces and a tube joining the parts. The first stethoscope was made by Rene Laennec.
It is used to check the number of hearts beats per minute in patients which gives clue to the doctors about the patients' state of health.
Q14. What is the importance of the parts labelled 'A' and 'B' in the figure given below ?

Solution
A is ureter which carries urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder. B is urinary bladder which stores urine temporarily before it is removed from the body.
Q15. Label any six of the parts of the heart A-G in the below figure. 

Solution
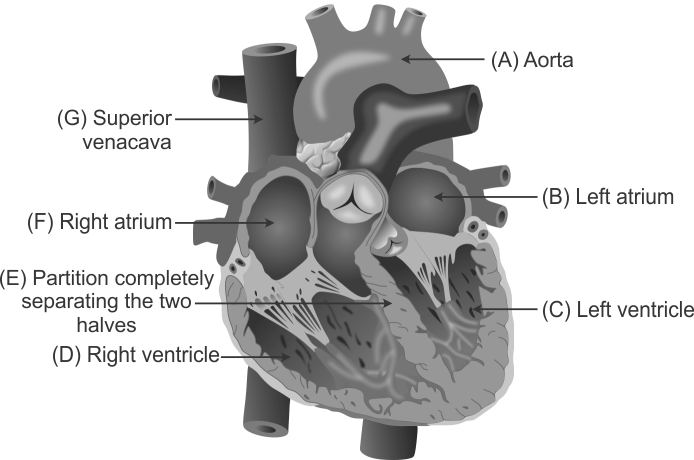 (label any 6 of these)
(label any 6 of these)
Q16. Diagrammatically show the blood circulation in human body.
Solution
Q17. (a) How many chambers are present in the human heart? Which heart chambers have thicker walls?(b) How many times does the heart of a resting person beat in a minute?
Solution
(a) There are four chambers in the human heart. They are two atria and two ventricles. The ventricles have thicker walls. (b) The heart beats 72 - 80 times per minute in a resting person.
Q18. Give reason: (i) Though pulmonary artery carries carbon-dioxide rich blood, it is still called as artery and not vein. (ii) Arteries have thick, elastic walls. (iii) Blood of all humans are red in colour.
Solution
(i) This is because pulmonary artery carries blood away from the heart and not towards it like a vein does. (ii) Since the blood flow through arteries rapidly at high pressure, the arteries have thick elastic walls. (iii) The red blood cells contain a red pigment called haemoglobin. The presence of haemoglobin makes blood appear red.
Q19. The opening and closing of stomata controls the passage of gases and water vapour into and out of the leaf.
Solution
True
Q20. Which blood cells act as soldiers of our body?
Solution
White blood cells acts as soldiers of our body. White blood cells fight against germs that enter our body either by destroying them or by producing antibodies against them; hence prevent us from infections.
Q21. What is the function of the region marked 'E' in the figure? 

Solution
The region marked 'E' is the partition between the chambers, called septum. It helps to avoid mixing up of blood rich in oxygen with the blood rich in carbon dioxide.
Q22. Label the parts shown as A-F in the below schematic diagram of circulation.

Solution
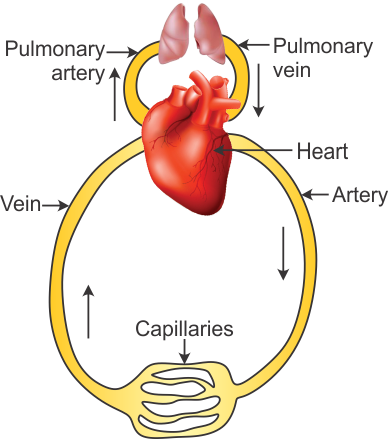
Q23. What are veins? What prevents the back flow of blood from veins?
Solution
Veins are vessels which carry carbon dioxide-rich blood from all parts of the body back to the heart. There are valves present in veins which allow blood to flow only towards heart and thus prevents the back flow of blood from veins.
Q24. Write any three functions of the fluid which flows in blood vessels.
Solution
The fluid which flows in blood vessels is blood. Its functions are: (i) It transports substances like digested food from the small intestine to the other parts of the body. (ii) It carries oxygen from the lungs to the cells of the body. (iii) It also transports waste materials for removal from the body.
Comments
Post a Comment