Q1. The petals attract insects for pollination.
Solution
True
Q2. Name three hard fruits.
Solution
Walnuts, almonds and peach are examples of hard fruits
Q3. (a) What do you understand by seed dispersal?(b) What happens to the seeds when fruits burst with sudden jerks?
Solution
(a) Seed dispersal refers to spread of seeds away from parent plant to a new growing location in order to prevent overcrowding.(b) When the fruits burst with sudden jerks, the seeds are dispersed and are scattered far from the parent plant.
Q4. Maple seeds are dispersed by _____________
Solution
wind
Q5. New plants can be obtained from the stem or branch of an existing plant by a method called _______________
Solution
cutting
Q6. Plants benefit by _______________
Solution
seed dispersal
Q7. What is self-pollination? Diagrammatically represent self-pollination.
Solution
The transfer of pollen from the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower is called self-pollination.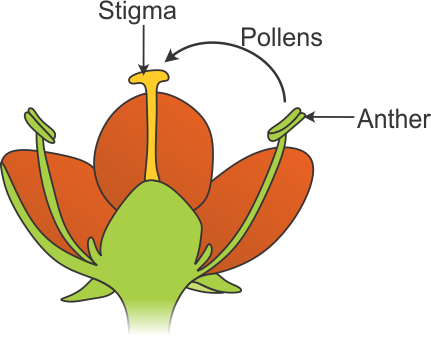

Q8. Why is vegetative propagation so called?
Solution
In vegetative propagation, new plants are produced from roots, stems, leaves and buds. Since, asexual reproduction is done through the vegetative parts of the plant, it is known as vegetative propagation.
Q9. How multiple fission is different from binary fission?
Solution
Multiple fission is the splitting of a cell into more than two cells of the same type whereas binary fission involves the splitting of a cell into two cells of the same type.
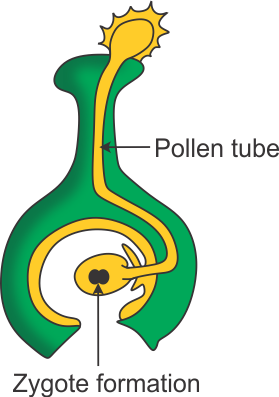
Q10. (a) Identify A, B, C and D in the below figure.
 (b) Name the parts of a pistil.
(c) How pollen tube is formed? What is its function?
(b) Name the parts of a pistil.
(c) How pollen tube is formed? What is its function?
 (b) Name the parts of a pistil.
(c) How pollen tube is formed? What is its function?
(b) Name the parts of a pistil.
(c) How pollen tube is formed? What is its function? Solution
(a) A - Germinating pollen grain B - Pollen tube C - Zygote formation D - Ovum
(b) A pistil consists of stigma, style and ovary.
(c) After pollination, the pollen grains germinate on the stigma. A thin pollen tube grows down from the pollen grain which penetrates the stigma, passes through the style and the enters the ovule. It carries two male gametes which fuses with the female gamete.
Q11. Mustard and rose are examples of _________________ flowers
Solution
bisexual
Q12. (a) How are seeds dispersed by animals? Give two examples of such seeds? (b) Diagrammatically represent fertilisation in plants.
Solution
(a) Some seeds are dispersed by animals, especially spiny seeds with hooks. They get attached to the bodies of animals and are carried to distant places. Examples are Xanthium and Urena. (b) Fertilisation (Zygote formation) in plants:

Q13. Name the process of reproduction occuring below. 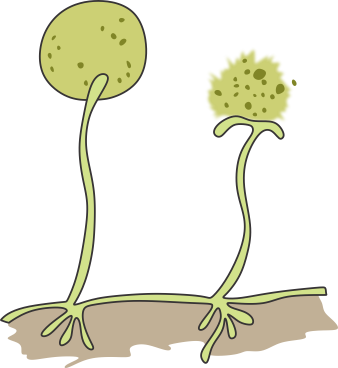 What is the advantage of this mode of reprodction. Write names of two plants which reproduce this way.
What is the advantage of this mode of reprodction. Write names of two plants which reproduce this way.
 What is the advantage of this mode of reprodction. Write names of two plants which reproduce this way.
What is the advantage of this mode of reprodction. Write names of two plants which reproduce this way.Solution
The process of reproduction shown above is Spore formation (in fungus). Each spore is covered by a hard protective coat to withstand unfavourable conditions such as high temperature and low humidity. So, they can survive for a long time. Under favourable conditions, a spore germinates and develops into a new individual. Plants such as moss and ferns can reproduce by means of spores.
Q14. Discuss the process of reproduction in yeast.
Solution
Yeast is a single celled organism which when provided with nutrients and the right temperature, gives out a small bulb-like projection called bud. The bud gradually grows and gets detached from the parent cell and forms a new yeast cell. The new yeast cell grows, matures and produces more yeast cells. This process continues to form a large number of yeast cells in a short time. 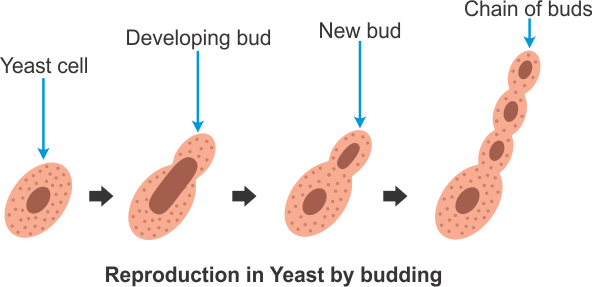

Q15. How the germination of seed takes place?
Solution
In the presence of moisture, the seed swells up and the shell bursts open. Its radicle goes into the soil to form the root. The plumule grows upwards and forms the shoot of the plant.
Q16. The flowers which contain either male reproductive part or female reproductive part are called __________________
Solution
unisexual flowers
Q17. Some seeds scatter their seeds when ripened. This phenomenon is called ________________
Solution
explosion
Comments
Post a Comment