Q1. Which of the two is moving faster (a) A car going over a distance of 100 km in 5 hours, or (b) A train covering a distance of 300 km in 6 hours?
Solution
Speed of the car = 100/5 = 20 km/h. Speed of the train = 300/6 = 50 km/h. Hence train is moving faster than the car.
Q2. The time between one new moon to the next is called?
Solution
The time between one new moon to the next is called a month.
Q3. Who found that a pendulum of a given length takes always the same time to complete one oscillation?
Solution
Galileo Galilie (A.D. 1564 - 1642) found that a pendulum of a given length takes always the same time to complete one oscillation.
Q4. The ages of stars and planet are often expressed in:
Solution
The ages of stars and planet are often expressed in billions of years.
Q5. Which of these is not a unit of speed?
Solution
Unit of speed contains any unit of length/unit of time. It can't be unit of time/unit of length.
Q6. If the speed of an object moving along a straight line keeps changing, its motion is said to be
Solution
If the speed of an object moving along a straight line keeps changing, its motion is said to be non-uniform motion.
Q7. A pendulum takes 10 sec to complete 5 oscillations. What is the time period of the pendulum?
Solution
Time Period = Time taken to complete one oscillationTherefore, T = Total time taken / Total oscillations = 10/5 = 2 seconds
Q8. An object is said to have a uniform motion if it moves
Solution
Uniform motion refers to motion at a constant speed in one way only, along a straight line path.
Q9. Time period of a simple pendulum depends upon:
Solution
Time period of a simple pendulum depends upon the length of the pendulum.
Q10. Which part of a second is called nano second?
Solution
A nanosecond is one billionth of a second.
Q11. A car moves with a speed of 40 km/h for 15 minutes and then with a speed of 60 km/h for the next 15 minutes. The total distance covered by the car is:
Solution
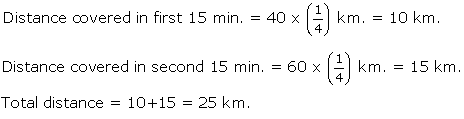
Q12. What is the average speed of second hand of a wrist watch? Given radius of the watch is 'r' metre.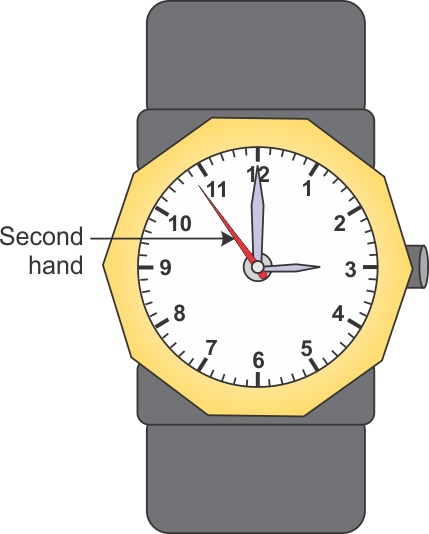

Solution
Distance covered by the second hand in 1 min. = 2πr metreWhere, r = radius of watchTherefore, Speed = 2πr / 1 = 2πr m/min
Q13. A dog runs behind you for 30 minutes and the distance covered by the dog is 3 km. What should be your minimum speed if dog was not able to bite you?
Solution
Your speed should be greater than that of the dog. Thus we will find speed of the dog and will come to know the minimum of your speed. Speed = Distance covered / Time taken = 3 / 30 = 1/10 km/min. Therefore, Speed = (1/10) x (1000/3600) = 1/36 m/s. Thus you must run at least above the speed of (1/36) m/s.
Q14. Calculate the time period of pendulum which oscillates 100 times in an hour.
Solution
Total time taken = 1 hour = 60 minutes = 3600 seconds Total no. of oscillations = 100 Therefore, Time Period of the pendulum = 3600/100 = 36 seconds
Q15. (i) What do you understand by uniform motion? Give some examples of uniform motion?(ii) Calculate the speed of the object at points A and B? At which point the speed is higher?
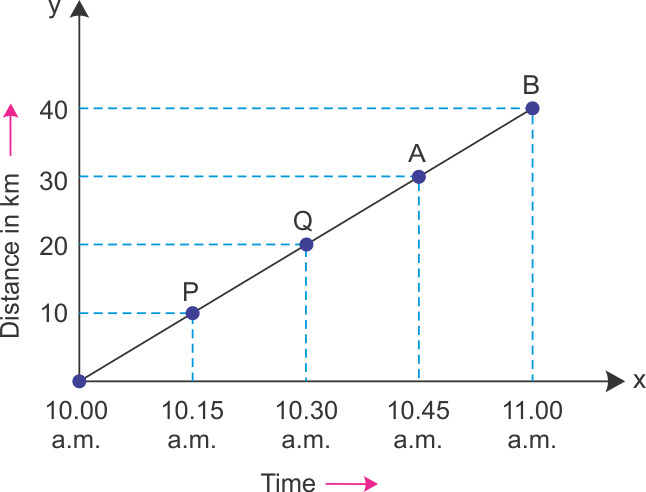

Solution
(i) An object moving in a straight line path with a constant speed along the same direction is said to be in the Uniform Motion Examples : (a) A bird flying one way only, along a straight path at a constant speed. (b) A ball rolling on a smooth horizontal track.(ii) Speed at A = Distance / Time = 30/45 = 2/3 km/min. Speed at B = Distance/Time = 40/60 = 2/3 km/min. Thus, the speed is same at both the points. Hence, the body is moving with a constant speed.
Q16. Name some of the instruments used in earlier times to measure time.
Solution
Some of the instruments used in earlier times to measure time are sundial, waterglass, and hourglass.
Q17. (i) Name two types of graphs other than line graphs. (ii) A body moves along a path. Its distance-time graph is shown below. How much time will it take to cover 100 km distance?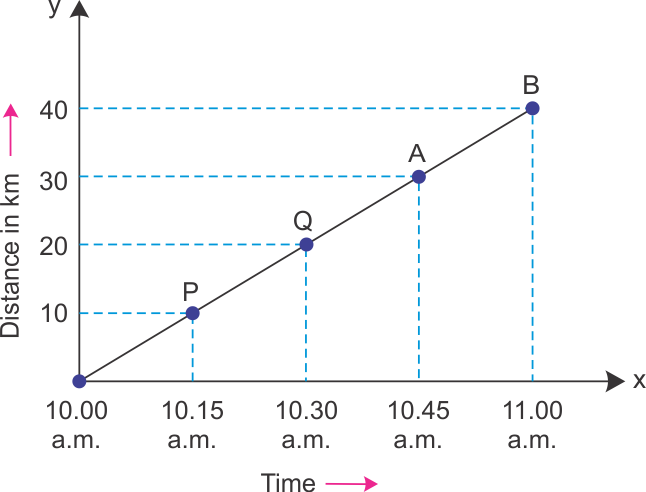

Solution
(i) Bar graph and pie chart. (ii) Speed = Distance/Time = 40 / 60 = 2/3 km/min Therefore, time required to travel 100 km is given by, Time = Distance/Speed = 100 / (2/3) = 100 x (3/2) = 50 x 3 = 150 minutes
Therefore, Time = 150 minutes = 2 hour 30 minutes
Q18. Find the speed of the car in km/hr between points O and A.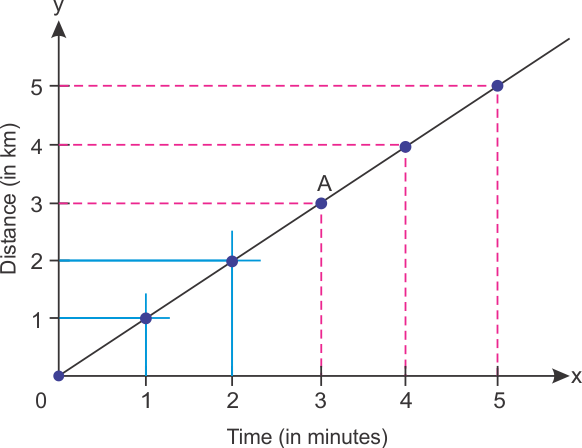

Solution
Total distance travelled = 3 km Total time taken = 3 minutes Speed = Total Distance Covered / Total Time Taken = 3/3 = 1 km/min
1 min = 1/60 hr
So, speed = 1/(1/60) = 60 km/hr
Q19. The distance between two stations is 560 km. A train takes 480 minutes to cover this distance. Calculate the speed of the train.
Solution
Distance = 560 km Time taken = 480 min = 480/60 = 8 hours So, Speed of train = distance travelled/time taken = 560 km/8 h = 70 km/h.
Q20. Show the shape of the distance-time graph for the motion in the following cases: (i) A bike moving with a constant speed. (ii) A car parked on a road side.
Solution
(i) A bike moving with a constant speed: 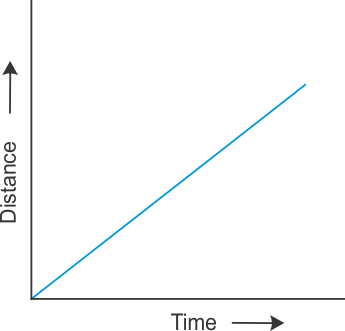 (ii) A car parked on a road side:
(ii) A car parked on a road side: 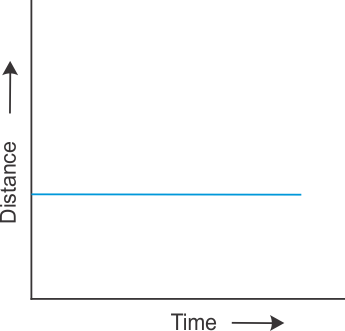
 (ii) A car parked on a road side:
(ii) A car parked on a road side: 
Comments
Post a Comment