Q1. The phenomenon that light travels in straight lines is called ________.
Solution
The phenomenon that light travels in straight lines is called rectilinear propagation of light.
Q2. What is dispersion of light?
Solution
Dispersion of light is the splitting of light into its component colors on passing through a dispersive medium e.g. prism.
Q3. If half part of a convex lens is covered, the focal length ___________ and the intensity of image __________.
Solution
If half part of a convex lens is covered, the focal length does not change and the intensity of image decreases.
Q4. The phenomenon of bouncing back of light falling on a smooth polished surface is known as ______.
Solution
The phenomenon of bouncing back of light falling on a smooth polished surface is known as reflection.
Q5. In spectrum obtained with prism which colour is deviated minimum?
Solution
Red colour is deviated minimum.
Q6. A disc with segments in rainbow colors is called
Solution
A disc with segments in rainbow colors is called Newton's disc.
Q7. A man is standing in front of a mirror sees his body as fat. The mirror is a _______.
Solution
Concave mirror forms magnified image for the object situated between centre of curvature and pole of the mirror.
Q8. Which kind of a mirror is used to see the enlarged image of the object?
Solution
Concave mirror is used to see the enlarged image of an object.
Q9. Dispersion of light by a glass prism takes place because:
Solution
Dispersion of light by a glass prism takes place because the light of different colors have different speeds in a medium. This results in different colours of light being refracted at different angles.
Q10. Why concave mirrors are used by dentists?
Solution
The concave mirrors are used by dentists because when the tooth is within the focus of concave mirror then an enlarged image of the tooth is seen in the concave mirror.
Q11. Why concave mirrors are used as reflectors?
Solution
The concave mirrors are used as reflectors because when lighted bulb is placed at the focus of concave reflector it produces powerful beam of light rays which helps us to see things up to a considerable distance in the darkness of night.
Q12. What is Newton's disc?
Solution
When a small circular disc with seven rainbow colours painted on it, is rotated fast, the colors get mixed together and the disc appears to be white. Such a disc is popularly known as Newton's disc.
Q13. Angle of reflection is equal to
Solution
Angle of reflection is equal to angle of incidence.
Q14. Convex mirror is also known as:
Solution
Convex mirror is also known as diverging mirror because it diverges the rays of light, which fall on its reflecting surface.
Q15. Why is Moon a non-luminous object?
Solution
Because it does not have light of its own but reflects light from the Sun.
Q16. The working of a lens is based on the phenomenon of ___________ of light.
Solution
The working of a lens is based on the phenomenon of refraction of light.
Q17. The nature of the image formed by a convex mirror is :
Solution
The nature of the image formed by a convex mirror is always virtual and erect.
Q18. The seven colors present in the rainbow are
Solution
The seven colors present in the rainbow are violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange, red.
Q19. Why do different colours of light refract at different angles in the formation of a spectrum?
Solution
Each colour of white light travels at a different speed in glass. This results in different colours of light being refracted at different angles.
Q20. How many colours are there in white light? Name the various colours of white light.
Solution
White light consists of seven colours. These colours are: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet.
Q21. Light is a form of energy produced by a
Solution
Light is a form of energy produced by a luminous object.
Q22. A _________ splits sunlight into seven colors.
Solution
A prism splits sunlight into seven colors.
Q23. The phenomenon in which left appears as right and vice versa in the image formation by a plane mirror is called ______.
Solution
The phenomenon in which left appears as right and vice versa in the image formation by a plane mirror is called lateral inversion.
Q24. The speed of light in vacuum is
Solution
The speed of light in vacuum is 3 x 108 m/s.
Q25. Why concave mirrors are used as shaving mirrors?
Solution
The concave mirrors are used as shaving mirrors because when the face is held within the focus of concave mirror then an enlarged image of the face is seen in the concave mirror.
Q26. Why convex mirror is used as a side mirror in scooters?
Solution
A convex mirror is used as a side mirror in scooters because it has large field of view.
Q27. Why the word 'AMBULANCE' is written on as in figure given below? 

Solution
This is because when we are driving in our car and see the hospital van coming from behind in our rear-view mirror, then we will get the laterally inverted image of the word and read it as AMBULANCE and give way to the vehicle.
Q28. Power of a lens is measured in
Solution
Power of a lens is measured in dioptre.
Q29. Define opaque objects. Give two examples of it.
Solution
An object which does not allow light to pass through it is called an opaque object. E.g., a book, a wooden table etc.
Q30. Light travels in a:
Solution
Light travels in a straight path.
Q31. What do the following figures indicate?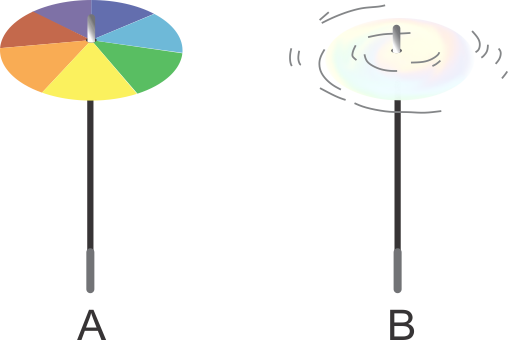

Solution
A disc with seven colours.
It appears white on rotating.
It is popularly known as Newton's disc.
Q32. The image which can be obtained on screen is called __________.
Solution
The image which can be obtained on screen is called real.
Q33. How can a convex lens be used as a magnifying glass?
Solution
To use a convex lens as a magnifying glass, the object to be viewed should be placed close to the convex lens so that a magnified and erect image of the small object can be seen on looking through the convex lens.
Q34. What are the uses of lenses?
Solution
Lenses are used to rectify visual defects of vision. Lenses are used in various optical instruments e.g. microscope, photographic camera, projector etc.
Q35. What are the two characteristic features of the image shown in the given figure?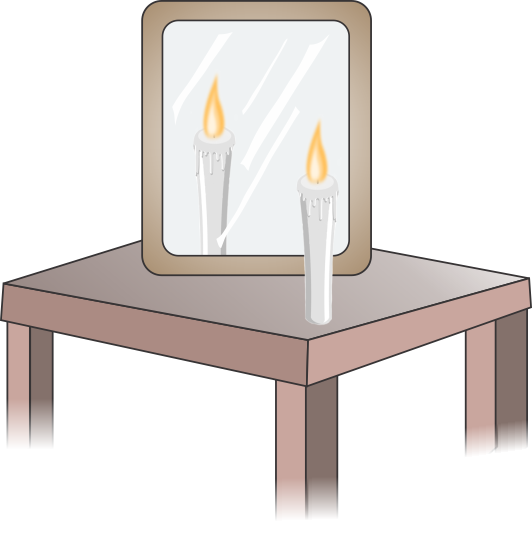

Solution
It shows that the image formed is erect and is of same size as the object.
Q36. Which lens is called as diverging lens and why?
Solution
A concave lens is called as diverging lens because it diverges or bends outward the light falling on it.
Q37. Give one similarity and one difference between a plane mirror and a convex mirror.
Solution
Similarity: Both, plane mirror and convex mirror, form a virtual and erect image of an object.
Difference: In a plane mirror, the image is of the same size as the object but in a convex mirror the image is always smaller than the object.
Q38. Which mirrors are used as side mirrors in scooters? Give reason.
Solution
Convex mirrors are used as side mirrors in scooters because convex mirrors can form images of objects spread over a large area. This helps the drivers to see traffic behind them.
Q39. What is the difference between the image formed by a concave mirror and convex mirror?
Solution
A concave mirror can produce a magnified as well as a diminished image whereas a convex mirror always produces a diminished image of an object.
Q40. When is a rainbow observed in the sky?
Solution
A rainbow is seen in the sky usually after the rain when the sun is low in the sky.
Q41. Which color light bends the most and which the least while passing through a prism?
Solution
Violet light bends the most and red light bends the least while passing through a prism.
Q42. Mention any three uses of plane mirrors.
Solution
(i) These are used in making periscopes. (ii) These mirrors are used as looking glass. (iii) These are fixed on the walls of certain shops to make the shops look bigger.
Q43. What is the difference between the real image and a virtual image?
Solution
An image which can be obtained on a screen is called a real image, while an image which cannot be obtained on a screen is called a virtual image.
Q44. What happens when a beam of light strikes a mirror?
Solution
On striking a mirror, the beam of light changes its direction.
Q45. Give an activity to show that light travels in a straight line.
Solution
(i) Take a lighted candle and place it on a table.
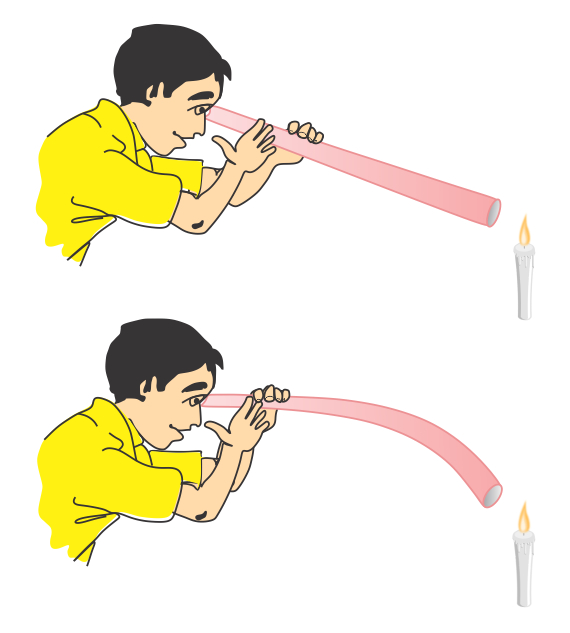 (ii) Look on it through a straight pipe and than through a bent pipe. (iii) You will find that the light can be observed through a straight pipe. This shows that light travels in a straight line.
(ii) Look on it through a straight pipe and than through a bent pipe. (iii) You will find that the light can be observed through a straight pipe. This shows that light travels in a straight line.
 (ii) Look on it through a straight pipe and than through a bent pipe. (iii) You will find that the light can be observed through a straight pipe. This shows that light travels in a straight line.
(ii) Look on it through a straight pipe and than through a bent pipe. (iii) You will find that the light can be observed through a straight pipe. This shows that light travels in a straight line.
Q46. Which lens is called as converging lens and why?
Solution
A convex lens is called as converging lens because it bends inward the light falling on it.
Q47. What is the difference between a concave and convex lens?
Solution
A convex lens is thicker at the centre but thinner at the edges whereas a concave lens is thinner in the middle but thicker at the edges.
Q48. Draw a diagram to show the splitting of white light into seven colours on passing through a prism.
Solution
Splitting of white light into seven colours on passing through the prism:
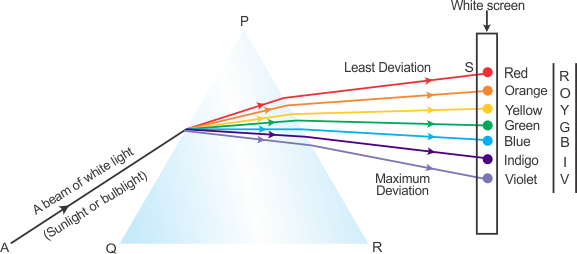

Comments
Post a Comment