Q1. Breaking of ozone to form oxygen is an example of which change?
Solution
A change in which new substances are formed is called a chemical change.
Q2. Crystallisation of sugar is an example of:
Solution
Crystallisation is formation of large crystals of pure substances from their solution. It is an example of physical change.
Q3. Name the process of depositing a layer of zinc on iron. Give two examples of objects on which zinc coating is done.
Solution
Galvanisation is the process of depositing a layer of zinc on iron. Rusting of an iron object can be prevented by the process of galvanization. Ex: Iron sheets used for making buckets and sheds are coated with zinc to prevent rusting.
Q4. A boy wants to experiment with sugar cubes. Select the method/s that cause sugar cube to change chemically only.(i) Chewing the sugar cube and digesting it(ii) Crushing the sugar cube(iii) Adding sugar cube in water(iv) Burning the sugar cube with a matchstick
Solution
The methods that cause sugar cube to only change chemically are:(i) Chewing the sugar cube and digesting it(iv) Burning the sugar cube with a matchstick
Q5. Name the change seen in the picture.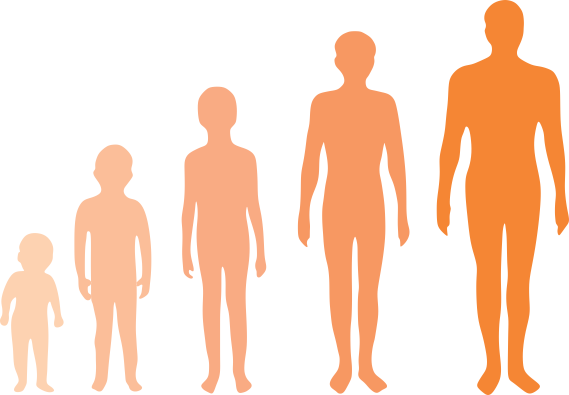

Solution
Growth is an example of chemical change as the change is irreversible.
Q6. Metal that can be deposited on iron to prevent rusting is/are:
Solution
Both chromium and zinc can be deposited on iron to prevent rusting.
Q7. Change in shape of an object denotes chemical change.
Solution
False.
Change in shape of an object denotes physical change.
Q8. Rusting can be prevented by:
Solution
Rusting can be prevented by painting the iron article. This will stop the contact of the article with air and moisture present in the air.
Q9. Explain how galvanization of an iron object prevents it from rusting.
Solution
In the method of galvanisation, surface of iron is covered with layer of more active metal like zinc. In this way, iron is prevented to come in contact with air and moisture which are required for rusting. Zinc metal does not undergo corrosion and hence prevents the rusting of iron.
Q10. Rusting of iron is a/an
Solution
Rusting of iron is an irreversible change.
Q11. Germination of seeds is a physical change.
Solution
False.
Germination of seeds is a chemical change.
Q12. Which of the following cannot be called a physical change?
Solution
Fermenting of cheese is a chemical change.
Q13. Magnesium burns in oxygen to form:
Solution
Magnesium burns in oxygen to form magnesium oxide.
Q14. Burning of a substance is an example of:
Solution
In a chemical change, new substances are formed. Burning of a substance involves formation of new products.
Q15. Writing on paper is a chemical change.
Solution
False.
Writing on paper is a physical change.
Q16. The iron pipes used in homes to carry water are coated with:
Solution
The iron pipes used in homes to carry water are coated with Zinc to prevent rusting.
Q17. Write an experiment to show that air and moisture are necessary for rusting.
Solution
Experiment to show that rusting of iron requires both air and water. We take three test tubes and put clean iron nail in each of the them. 1.In the first test tube containing iron nail, we put some anhydrous calcium chloride and closed its mouth with a tight cork. The anhydrous calcium chloride is added to absorb water or moisture from the damp air present in the test tube and make it dry. In this way, the iron nail in the first test tube is kept in dry air. This test tube is kept aside for about half an hour. After one week, we observe that there is no rust on the surface of iron nail. This shows that rusting of iron does not take place in air alone. 2.In the second test tube containing iron nail, we put boiled distilled water. Boiled distilled water does contain any dissolved air or oxygen in it. A layer of oil is put over boiled water in the test tube to prevent the outside air from mixing with boiled water. In this way, the iron nail in the second test tube is kept in air free, boiled water. The mouth of this test tube is closed with a cork and it is kept aside for about a week. After one week, we observe that no rust is there on the surface of iron nail. This shows that rusting of iron does not take place in water alone. 3.In the third test tube containing an iron nail, we put unboiled water so that about two-thirds of the nail is immersed in water and the rest is above the water, exposed to damp air. In this way, the iron nail has been placed in air and water together. The mouth of this test tube is closed with a cork and it is kept aside for about a week. After one week, we observe that red brown rust is seen on the surface of iron nail kept in the presence of both air and water.
Q18. Mixing of lime in water is a chemical change.
Solution
True
Q19. Neutralisation is a _____________ change.
Solution
Neutralisation is a chemical change.
Q20. Which of the following is not a physical change?
Solution
Rusting of iron is a chemical change.
Q21. Which of the following is a physical change?
Solution
Boiling of water is a physical change since it only involves a change in state. There is no new compound formed.
Q22. Rusting can be prevented by depositing a layer of a metal on iron.
Solution
True
Q23. Name the change seen in the picture.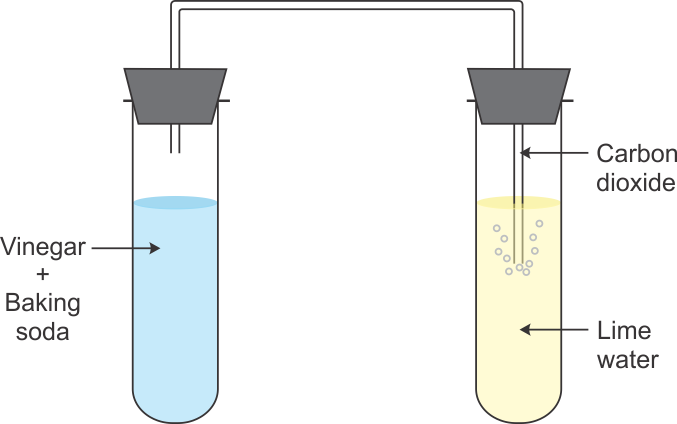

Solution
When carbon dioxide is passed through lime water, calcium carbonate is formed, which makes lime water milky. It is an example of chemical change.
Q24. Which of the following increases the rate of rusting?
Solution
The presence of salts in water increases the rate of rusting.
Q25. When your dog rips up your homework, it is a physical change.
Solution
True
Q26. Regular coating of paint prevents iron articles from
Solution
Regular coating of paint prevents iron articles from rusting.
Q27. Name the change as seen in the image.

Solution
Rusting of iron is an example of chemical change.
Q28. In galvanisation, the iron metal is coated with which metal to prevent rusting?
Solution
In the process of galvanisation, the iron metal is coated with zinc to prevent rusting.
Q29. Breaking of rock is an example of __________________ change.
Solution
Breaking of rock is an example of physical change.
Q30. Rusting of iron is faster in coastal areas than in deserts. Give reason.
Solution
Since content of moisture in the air in coastal areas is higher than in the air in deserts so, the process of rusting becomes faster in the coastal areas.
Q31. Burning of a match stick is an example of _________________ change.
Solution
Burning of a match stick is an example of chemical change.
Q32. Differentiate between physical and chemical changes (four points).
Solution
Physical changes
Chemical changes
1. In a physical change, only physical properties such as physical state, colour, volume etc. of the reacting substance undergo change. Chemical properties remain unchanged.
1. In a chemical change, the chemical composition and chemical properties of the reacting substances undergo change.
2. No new substance is formed.
2. One or more new substances are formed.
3. These are temporary changes that can be easily reversed.
3. These are permanent changes and cannot be reversed back.
4. The original form of the substance can be obtained easily by simple physical methods.
4. The original substances cannot be obtained by simple physical methods.
Q33. Explosion of a cracker is a chemical change. Explain.
Solution
Explosion of a cracker is a chemical change because the explosive reactants are transformed into gaseous products along with heat, light and sound which cannot be reversed. Hence, it is a chemical change.
Q34. Mixing of water colours is a ________________ change.
Solution
Mixing of water colours is a physical change.
Q35. Identify the chemical change.
Solution
Formation of manure from leaves is a chemical change since it involves the formation of a new product with different properties.
Q36. What is photosynthesis? Why is it considered a chemical change?
Solution
The process in which carbon dioxide reacts with water in presence of chlorophyll and sunlight to produce carbohydrates (glucose) and oxygen is known as photosynthesis. New products (glucose and oxygen) are obtained during photosynthesis, thus it is a chemical change.
Q37. Rust is:
Solution
Rust is different in composition from iron.
Q38. Iron articles dipped in oil are more prone to rusting.
Solution
False.
Iron articles dipped in oil are protected from rusting.
Q39. Vaporisation of candle wax is a ______________ change.
Solution
Vaporisation of candle wax is a physical change.
Q40. Melting of iron in furnace is a chemical change.
Solution
False.
Melting of iron in furnace is a physical change.
Q41. Which of the following is a physical change?
Solution
Physical changes are reversible changes. No new substances are formed in these changes.
Q42. An apple undergoes change in colour after some days. This is an example of _______________ change.
Solution
An apple undergoes change in colour after some days. This is an example of chemical change.
Q43. Cutting a paper into pieces is a physical change.
Solution
True
Q44. Identify the type of change in each of the following: (i) Burning of candle (ii) Lightening of bulb (iii) Preparation of food by green plants (iv) Volcanic eruption (v) Lightening (vi) Spinning of wheels of cycle
Solution
(i) Burning of candle: Chemical change (ii) Lightening of bulb: Physical change (iii)Preparation of food by green plants: Chemical change (iv)Volcanic eruption: Chemical change (v) Lightening: Physical change (vi)Spinning of wheels of cycle: Physical change
Q45. The iron pipes we use in our homes to carry water are galvanised to prevent rusting.
Solution
True
Q46. The same substance can undergo a physical change or a chemical change depending upon the conditions. Explain with an example.
Solution
The melting of wax is a physical change but burning of wax is a chemical change. So, the same substance wax can undergo both physical and chemical change. On melting, only change in the state of wax occurs but on burning wax, it produces carbon dioxide gas, water vapour, soot, heat and light. Hence, it is a chemical change.
Q47. What is crystallisation? Give its main use.
Solution
Crystallisation is the process of obtaining large crystals of pure substances from their solution. Crystallisation is a technique used to purify solid compounds.
Q48. Identify the following changes as physical or chemical change. (a) Log of wood burns to form ash. (b) Steam condenses to form water. (c) A bicycle chain rusts. (d) Water is absorbed by a paper towel. (e) A piece of a mango rots on the ground. (f) Dissolving sugar in water.
(g) Eggs turn into omelet.
(h) Stretching metals to form wires.
Solution
Physical Change
Chemical Change
(i) Steam condenses to form water. (ii) Water is absorbed by a paper towel.
(iii) Dissolving sugar in water.
(iv) Stretching metals to form wires.
(i) Log of wood burns to form ash. (ii) A bicycle chain rusts. (iii) A piece of a mango rots on the ground. (iv) Eggs turn into an omelet.
Q49. The brown layer is formed when an iron article is left exposed in an open area. Name the process and explain it. What is its effect on the object? Write the chemical equation to show the process of rusting of iron.
Solution
If we leave a piece of iron in the open for some time, it acquires a coating of brownish substance. This substance is called as rust and the process of its formation is called rusting. This is the only change that effects iron articles and slowly destroy them. Since iron is used in making bridges, ships, cars, truck and many other objects. Rusting weakens the structures of iron objects and cuts short their life. Following is the chemical equation to show the process of rusting of iron: Iron (Fe) + Oxygen (O2, from the air) + water (H2O)  rust (iron oxide Fe2O3)
rust (iron oxide Fe2O3)
 rust (iron oxide Fe2O3)
rust (iron oxide Fe2O3)
Q50. A pinch of baking soda is added to vinegar in a test tube. A hissing sound is heard and bubbles of gas are observed. This gas is passed through freshly prepared lime water. (i) What is lime water? (ii) What happens to lime water when gas is passed through it? (iii) Identify the gas evolved.
(iv) Write all the reactions involved.
Solution
(i) Lime water is calcium hydroxide solution.
(ii) When the gas evolved is passed through lime water, then lime water turns milky. (iii) The turning of lime water milky shows the presence of carbon dioxide because when CO2 is passed through lime water, white solid substance 'calcium carbonate' is formed which makes lime water milky. (iv) A. Vinegar(Acetic acid) + Baking soda(Sodium hydrogen carbonate)  Carbon dioxide + sodium acetate + Water (H2O) b. Carbon dioxide (CO2) + Lime water [Ca(OH)2]
Carbon dioxide + sodium acetate + Water (H2O) b. Carbon dioxide (CO2) + Lime water [Ca(OH)2]  Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) + Water (H2O)
Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) + Water (H2O)
 Carbon dioxide + sodium acetate + Water (H2O) b. Carbon dioxide (CO2) + Lime water [Ca(OH)2]
Carbon dioxide + sodium acetate + Water (H2O) b. Carbon dioxide (CO2) + Lime water [Ca(OH)2]  Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) + Water (H2O)
Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) + Water (H2O)
Q51. Why are cooking utensils usually made of stainless steel?
Solution
Cooking utensils are usually made of stainless steel as it does not rust at all.
Comments
Post a Comment